This page is a high-level overview of the material in our Introduction to Geocomputing class. It will give you a flavour of the sort of data we use and the exercises we set.
Our approach
We don't actually teach this module, but it drives everything we do.
Everything is implemented in code: figures, charts, examples, etc.
Everything is reproducible.
Everything is in version control.
Data must be digital and carry metadata.
Important workflows belong in code.
Manipulating and visualizing data
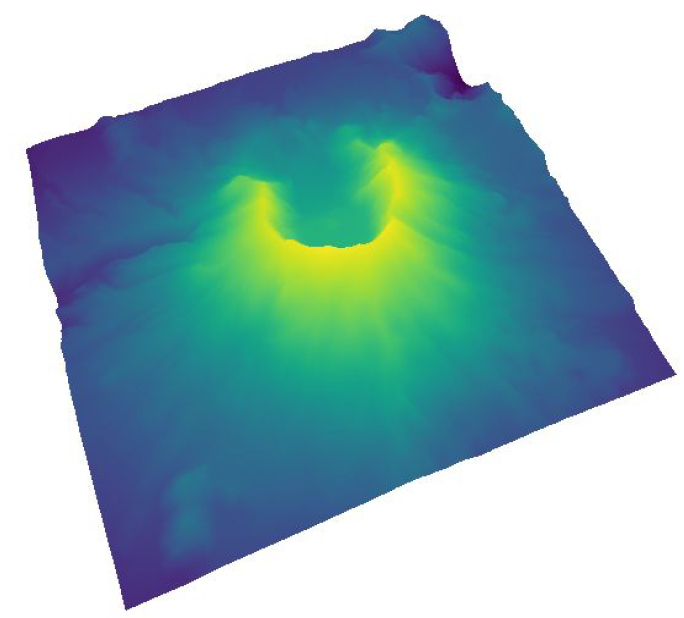
Follow-along exercise: Make a topography map in 5 lines of code (right).
Follow-along exercise: A lightweight 3D seismic visualization.
Variables and assignment
Introduction to Python command line.
Basic assignment syntax and dynamic typing.
Asking for help. Finding help online.
Native data types
int and float (and complex); why so many kinds of numbers?
str.
Type casting.
String methods, strings as collections. Indexing and slicing.
String formatting anf f-strings.
Exercise: text processing practice manipulating formation names.
Operators and expressions
Mathematical operations, comparison operators, booleans.
Augmented assignment, multiple assignment.
Copies and pointers.
Exercise: some gentle rock physics.
Data collections and data structures
list — indexing again, slicing again, striding, nested lists.
Exercise: Getting ages from the geologic timescale. Practice indexing.
tuple and set
dict — mappings of key:value pairs.
Exercise: Stratigraphic column: storing, retrieving and modifying entries in dicts.
Exercise: Introduction to visualizing well logs: line plots vs scatter plots.
Flow control
Iteration and iterables: for and while.
Exercise: compute impedance and reflectivity in a well.
List comprehensions.
Exercise: convert for loops into list comprehensions.
Making decisions: if-elif-else statements.
Exercise: create a pay flag on a gamma-ray log.
Getting data, part 1
Reading and writing text files.
Exercise: create a dictionary of well tops from a ‘broken’ input text file.
Functions
Built-in functions, and importing modules.
The anatomy of a function. Syntax, docstrings.
Exercise: write a function that computes an impedance log.
Exercise: write a function that computes reflection coefficients.
Exercise: write a function that computes formation thicknesses.
Sharing code via modules, importing and using modules.
Exercise: Getting data from a sidewall core analysis report (csv file).
Exercise: Get geological ages by processing pages.
The Python standard library.
External Python packages and PyPi.



 Except where noted, this content is licensed
Except where noted, this content is licensed